2. 旱区现代农业水资源高效利用教育部工程研究中心, 宁夏 银川 750021;
3. 省部共建西北土地退化与生态恢复国家重点实验室, 宁夏 银川 750021;
4. 宁夏回族自治区黄河水联网数字治水重点实验室 宁夏 银川 750021
2. Engineering Research Center for Efficient Utilization of Modern Agricultural Water Resources in Arid Regions, Ministry of Education, Yinchuan, Ningxia 750021, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Land Degradation and Ecological Restoration in Northwest China, Yinchuan, Ningxia 750021, China;
4. Key Laboratory of the Internet of Water and Digital Water Governance of the Yellow River in Ningxia, Yinchuan, Ningxia 750021, China
土壤盐渍化和水资源短缺是制约全球农业生产和粮食安全的关键障碍因子[1-2]。据统计,全球现有盐碱土地面积约1.10×109 hm2,约占全球耕地面积(1.50×1010 hm2)的73%,且这一比例仍呈逐年上升态势[3]。土壤盐渍化不仅会破坏土壤结构,影响微生物群落,还会引发作物减产、造成地下水污染、土地荒漠化等一系列问题[4-5]。因此盐碱地的综合利用成为保障耕地安全的有效途径之一。
土壤盐渍化的形成受自然因素与人为因素的共同作用,地下水作为水循环的重要组分[6]以及盐分传输、累积和排泄的主要载体[7],其动态变化对土壤盐渍化影响尤为显著。有研究指出,地下水通过赋存、补给、排泄和冻融等过程影响土壤水的时空分布规律,驱动土壤溶质运移,进而诱发土壤盐渍化[8-9]。基于此,地下水调控就成为一种盐碱地障碍消减的有效手段。许多学者[10-13]在土壤水盐动态变化、灌区水资源优化配置、灌排模式下改良盐渍土等方面开展研究,并在盐渍土分布区域得到验证与应用。《2022年联合国世界水发展报告》中指出一些地区浅层含水层在很大程度上未充分开发,Haj-Amor等[14]详细阐述灌溉条件下浅层地下水动态变化,评估地下水排水系统对土壤脱盐的影响,为干旱地区盐渍化农田恢复提供参考;中央支持各级城乡建设排水设施、统筹水资源利用和智慧平台建设,一些地区通过暗管排水[15]、井渠结合等措施控制地下水位[16],并将这部分地下水用于灌溉,在优化水资源、改良盐碱地方面取得成效。
21世纪以来,关于地下水调控对土壤水盐动态演变过程及其相互作用机制的研究已取得丰硕成果,在土壤盐渍化成因[17]、水盐运移规律[18]、盐碱综合治理[19-21]、旱区地下水利用等[22]方面均有相关文献阐述。然而,目前亟需通过可视化手段系统梳理该领域已有研究成果、整合有价值信息、明晰该领域研究热点,为盐渍化土壤综合利用提供数据支撑。鉴于此,基于文献计量学方法,通过Citespace和Vosviewer软件对该领域进行定量分析和可视化展示,旨在全面把握其研究脉络、演变特征和发展态势,以期为盐碱土地障碍削减和地下水优化调控提供理论依据和实证参考。
1 数据与方法 1.1 数据来源英文文献选取自Web of Science核心数据库(WoS),以“TS=((groundwater OR groundwater regulation OR groundwater dynamics OR groundwater depth OR culvert drainage OR well irrigation and well drainage) AND soil water salinity)”作为主题词进行检索。设置时间范围为2000年1月1日至2022年12月31日,筛选数据类型为“Article”和“Review”,语种则选择“English”。中文文献则收集自中国知网数据库(CNKI),借助高级检索功能以“(地下水+地下水调控+地下水动态+地下水埋深+暗管排水+井灌井排)×(土壤水盐)”作为主题词,时间范围为2000年1月1日至2022年12月31日,检索范围为“总库”,筛选数据类型为“学术期刊”和“学位论文”。经过逐篇阅读并剔除干扰文献后,最终得到728篇中文文献与1921篇英文文献。
1.2 分析方法借助VOSviewer和CiteSpace软件对研究机构及发文作者进行共现与聚类,并对主要关键词进行聚类与突发性检验[23];同时,结合Scimago Graphica对研究领域主要参与国家的发文数量及其合作关系进行地理可视化展示;Microsoft Excel 2016与Origin 2021进行发文数量和学科分布的统计分析及图形绘制。
2 结果与分析 2.1 发文数量及其发文趋势2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的中英文文献数量均整体呈现波动上升趋势(图 1)。其中,英文文献的数量始终处于领先地位,其年际增长率(k=6.92)明显大于中文文献(k=2.07)。

|
图 1 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的中英文文献发文数量与发文趋势 Figure 1 Number and trend of Chinese and English literature publications in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域SCI发文数量排名前五的国家分别为中国(467篇)、美国(380篇)、澳大利亚(297篇)、印度(149篇)和埃及(81篇)。其中,中国和美国占据主导地位,且从2015年开始,中国在该领域的发文数量已明显超越美国(图 2)。
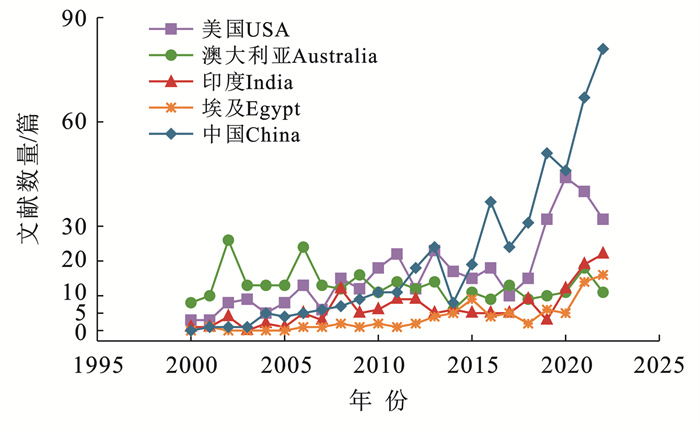
|
图 2 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域主要发文国家的年度SCI发文数量 Figure 2 Annual SCI publications by major countries in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域主要形成以中美国家为关键核心的研究格局(图 3)。其中,中国与美国、德国、澳大利亚等国家的合作联系较为密切。

|
图 3 2000—2022年英文文献主要发文国家的地理分布、发文数量及其相互联系 Figure 3 Geographical distribution, number of publications, and their interrelationships of main publishing countries in English publications during 2000—2022 |
英文文献发文数量排名前5的研究机构分别为Chinese Academy of Sciences(153篇),China Agricultural University(57篇),CSIRO Land and Water(49篇),University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(48篇),CSIRO(34篇),各机构间的联系与合作较为紧密(图 4a)。中文文献中的主要研究机构则分别是内蒙古农业大学(60篇)、新疆农业大学(29篇)、西安理工大学(26篇)、石河子大学(23篇)与新疆大学(22篇)(图 4b)。其中,多数机构为与农业相关的高校或单位。然而,国内研究机构间的合作较为松散,联系较为微弱,今后还需进一步拓宽研究视野,持续开展多渠道、全方位、深层次的合作交流。
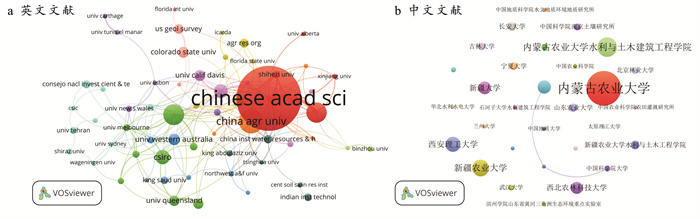
|
图 4 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的主要发文机构知识图谱 Figure 4 Knowledge map of main publishing organizations in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
图 5为2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的主要发文作者知识图谱。由图 5可知,中英文文献中相关作者间的合作强度均较为微弱,呈现出多核心、分散式的结构模式;核心作者群之间的研究合作关系则较为密切,而多数的学者尚处于独立研究状态。
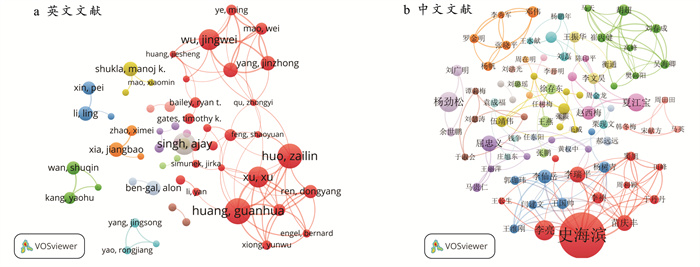
|
图 5 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的主要发文作者知识图谱 Figure 5 Knowledge map of main authors in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
核心作者是促进学科发展以及推动领域创新的中坚力量。基于普赖斯定律[24],以第一作者身份发表的最多文章数量(Npmax,取21)为基础,对该领域在2000—2022年的核心作者所对应的最少发文数量(Mp)进行计算,见公式(1):
| $ M_p=0.749 \sqrt{N_{p \max }} $ | (1) |
根据计算结果(Mp=4)可知,中英文文献分别包含43,130个核心作者。其中,史海滨(内蒙古农业大学,21篇)和黄冠华(中国农业大学,20篇)位居首位(表 1)。黄冠华团队的主要研究领域包括多尺度农业水文与伴生过程模型与模拟、农田节水减排控盐理论与技术等[25-29];史海滨团队的主要研究方向涵盖内蒙古河套灌区土壤水盐时空分布规律及其变异特征、盐碱农田灌排协同调控技术及其模式应用等[30-33]。
|
|
表 1 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域发文数量排名前5的核心作者 Table 1 Core authors ranking top 5 in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
此外,在英文文献中,霍再林(中国农业大学,19篇)团队主要聚焦“作物需水—土壤水(盐)—地下水”间的协同互馈机制[34-35]。而在中文文献中,杨劲松团队(中国科学院南京土壤研究所,8篇)主要开展河套灌区盐碱农田地力提升与健康保育等方面的研究[36-38]。
2.5 主要学科分布2000—2022年该领域相关文献的学科分布见图 6。其中,英文文献涉及的学科主要为水资源(26.18%)、环境科学生态学(23.22%)、农业(20.64%)、与地质学(11.83%);中文文献中占比最大的学科则是农业基础科学(30.05%)、农艺学(27.76%)、自然地理学和测绘学(15.92%)以及农业工程(11.09%)。今后的相关研究还需加强学科交流与资源流动,持续推动理论创新与技术提升,以进一步深化该领域在新时期战略背景下的高效高质服务及其可持续发展。
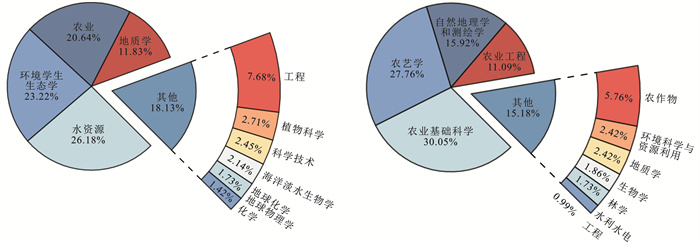
|
图 6 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的主要学科分布 Figure 6 Distribution of major disciplines in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
通过调整阈值“minimum number of occurrences of a keyword=10”,最终获得中英文文献关键词个数分别为54,334。其中,排名前10的高频英文关键词为:“salinity”“groundwater”“water”“irrigation”“management”“soil”“growth”“salinization”“soil salinity”“quality”;相应的高频中文关键词则主要有:“水盐运移”“数值模拟”“河套灌区”“土壤盐分”“膜下滴灌”“暗管排水”“地下水”“土壤盐渍化”“地下水埋深”“土壤”。
进一步将2000—2022年该领域的中英文关键词分别划分为5个和6个热点主题(图 7—8)。其中,中文文献主要聚焦:①盐渍化灌区土壤水盐运移对灌排协同调控的响应与模拟[39-40];②不同工程实践情景下的农田土壤水盐动态及其数值模拟[41-42];③灌溉方式对盐渍化土壤水盐运移与作物产量的影响效应[43-44];④滨海地区地下水开发利用模式下的土壤水盐运移与分布[45];⑤河套灌区地下水时空动态变化与土壤水盐空间分异特征[46-47]。英文文献则重点关注:①盐渍化灌区土壤水盐时空分布特征与溶质迁移转化规律[48];②盐渍化灌区土壤水盐调控技术及其对作物产量影响效应[49];③盐渍化灌区地下水资源的地球化学特征与环境污染防控[50];④滨海地区灌溉类型对土壤盐分运移与作物生长影响效应[51];⑤基于遥感和模型的盐渍化土壤时空演变特征与调控管理[52];⑥盐渍化灌区的土壤水力特征参数反演及其空间变异特性[53]。
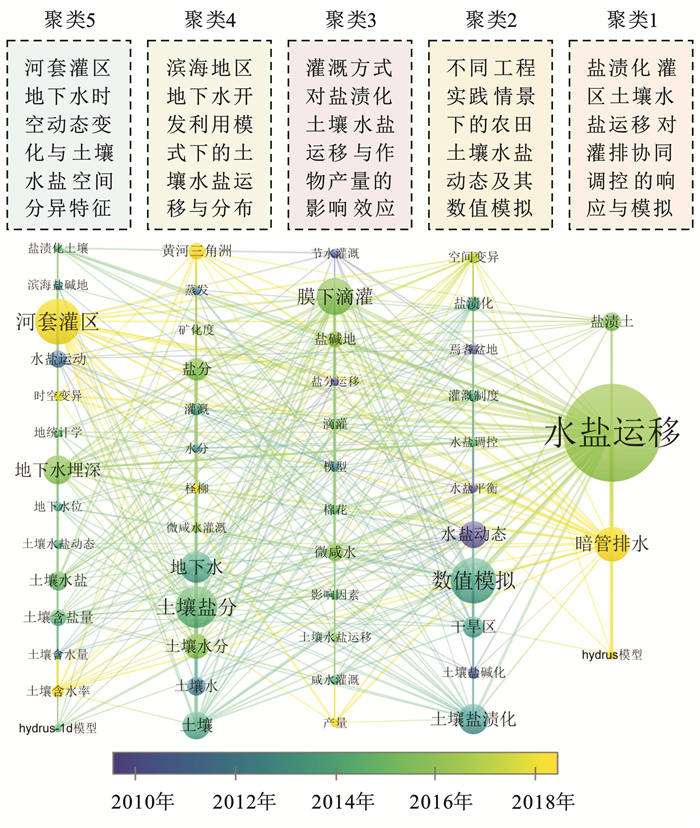
|
图 7 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的主要中文关键词及其主题聚类 Figure 7 Main Chinese keywords and their theme clustering in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
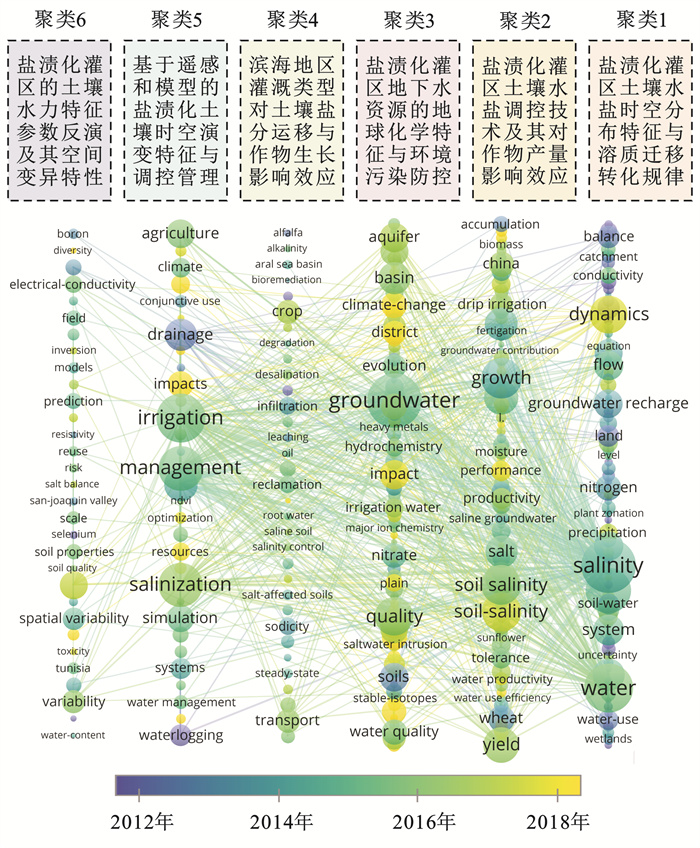
|
图 8 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的主要英文关键词及其主题聚类 Figure 8 Main English keywords and their theme clustering in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
对2000—2022年该领域的中英文文献分别进行突发性检验分析,均可获得15个突现词(表 2—3)。其中,英文关键词中的“dryland salinity”“water use”“growth”“drainage”“soil water”主要于2002年开始显现,重点关注地下水对土壤水盐的影响机理及其运移机制[54-55];“murray basin”“accmulation”“soils”“model”“system”“area”等关键词则在2006年左右陆续突现,着重应用数值模型对“土壤水—地下水—地表水”的相互作用关系及溶质运移机理进行深入剖析[56-57];2016年至今突现的关键词主要有“stable isotopes”“crop”“precipitation”“productivity”,同位素示踪等先进技术成为解析“土壤圈—大气圈—水圈—生物圈”互作关系的有力工具[58]。
|
|
表 2 2000—2022年英文文献的关键词突发性检测 Table 2 Keyword burst detection in English literature during 2000—2022 |
|
|
表 3 2000—2022年中文文献的关键词突发性检测 Table 3 Keyword burst detection in Chinese literature during 2000—2022 |
中文关键词中的“水盐动态”和“模型”于2000年突现,开始借助数值模型对灌排情景下的非饱和带土壤水盐及地下水动态进行模拟和预测[59];“数值模拟”“焉耆盆地”“水盐监测”“盐分运移”“土壤盐分”“影响因素”等关键词则主要在2004—2012年突现,在田间长期监测的同时,进一步结合算法优化与模拟建立,对盐渍化灌区,特别是地下水浅埋区的土壤水盐动态进行精准模拟[60];于2014年左右,“作物”“柽柳”“土壤水”“盐分”“滴灌”“灌水量”“暗管排水”等关键词陆续突现,重点聚焦土壤盐碱成因及其综合治理[21]、盐碱农田的灌溉方式与灌溉制度优化[61]、灌排协同调控及其模式优选[62]等。
以时间年份作为X轴,聚类标签为Y轴,分别绘制2000—2022年该领域的中英文关键词聚类时间线谱(图 9—10)。可以看出,其聚类模块值(Q)大于0.30,平均轮廓值(S)大于0.70,表明聚类结构合理且可靠。
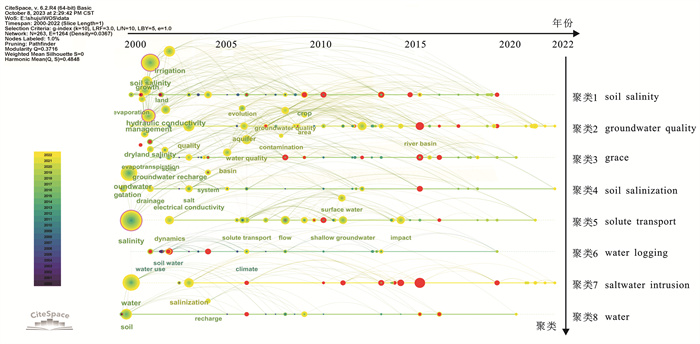
|
图 9 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的英文关键词时间线及其主题聚类 Figure 9 English keywords timeline and their theme clustering in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |

|
图 10 2000—2022年地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响领域的中文关键词时间线及其主题聚类 Figure 10 Chinese keywords timeline and their theme clustering in field of impact of groundwater dynamics on soil water and salt during 2000—2022 |
其中,英文关键词可分为8个聚类,分别为“soil salinity”“groundwater quality”“grace”“soil salinization”“solute transport”“water logging”“saltwater intrusion”“water”;中文关键词则具有10个聚类,分别是“膜下滴灌”“土壤盐渍化”“数值模拟”“土壤盐分”“黄河三角洲”“水盐运移”“水盐动态”“盐渍化”“人工神经网络”“咸水灌溉”。
3 结论(1) 总体上看,国内外地下水对土壤盐渍化影响的研究均呈波动上升趋势其中。其中,英文文献发文量较高。
(2) 国内外进行地下水对土壤盐渍化影响研究的主要有:机构(中国科学院、中国农业大学、澳大利亚联邦科学与工业研究组织水土资源所、内蒙古农业大学等)、核心作者(黄冠华、霍再林、史海滨、杨劲松等)、地区(中国、美国、澳大利亚等国)、学科(水资源、环境科学生态学、农业基础科学和农艺学)。其研究重点不尽相同,中国团队聚焦盐碱地综合利用和地下水调控方面开展研究。此外,该领域主要形成以中美国家为关键核心的研究格局。其中,中国与美国、德国、澳大利亚等国家的合作联系较为密切。因此,需进一步加强国际交流,促进该领域高速、多元发展。
(3) 地下水动态变化对土壤盐渍化影响相关领域研究主题日益演变,前沿课题不断更替。国外学者研究热点为盐渍化灌区土壤水盐时空分布特征与溶质迁移转化规律、盐渍化灌区土壤水盐调控技术及其对作物产量影响效应、盐渍化灌区地下水资源的地球化学特征与环境污染防控等方面,呈现跨学科、多层次、全方位的特点,推动自身发展的同时,带动新兴学科快速发展;我国主要聚焦在盐渍化灌区土壤水盐运移对灌排协同调控的响应与模拟、不同工程实践情景下的农田土壤水盐动态及其数值模拟、灌溉方式对盐渍化土壤水盐运移与作物产量的影响效应等方面,主线脉络由单一化向多元化逐步完善,研究热点充分考虑中国农业生产需求,由盐渍化基础理论逐步过渡到盐碱地综合利用提质增效。同时,理论与工程结合逐步向生产力转化的研究将是今后的关注重点。
4 展望国内外学者关于地下水动态变化对土壤水盐影响进行了许多探索,通过梳理该领域研究热点,研究仍存在地下水调控过程不明确、盐渍化改善效果不持续等不足。展望未来,为有效管控土壤盐渍化危害,扎实推动土壤质量持续改善,深入贯彻生态文明思想,有如下5个方面需要强化和完善:
(1) 优化流域水资源配置,提高水土资源有效利用率。随着人口增长和经济发展,城市群特别是中心城市的水资源保障问题将日益突出,很多国家和地区面临较大的水资源供给压力。加强水资源优化配置和科学调度,满足经济社会发展刚性需求。如,中国西北地区蒸发强烈,春季及作物生育期地下水水位高,易造成地表盐分累积形成土壤盐渍化,使作物受到盐胁迫。然而,当前我国灌溉水、再生水利用尚存在利用不充分、配置水平不够高等问题。因此,将区域地下水适宜水位埋深作为约束条件,提出合理的调控方案,满足作物需水量的前提下,通过一定的排水措施(暗管与竖井排水工程、排水沟等)降低地下水位,以此推动再生水利用,达到减少盐渍化和满足作物生长的目的,为防治盐渍化,实现生态环境保护及管理提供新思路。
(2) 建立健全水资源开发管理和数据资源体系。数据赋能是实现盐渍化综合利用的重要方式,当前已构建“国家地下水监测工程”,应用包括基于北斗的自动化数据传输技术、浅层地下水连续多通道分层监测井等科技成果,实现对水位和水质的有效监测,强化流域水资源统一管理。尽管如此,盐渍化程度高的干旱地区在涉及水质分析方面比较薄弱。因此,未来应因地制宜制定地下水分级标准,为水资源开发利用提供指标参考。此外,应进一步结合地区经济、农业生产特点、水文地质、工程地质,依托国家发展规划,对地区水资源可开采量、补给排泄量、水化学类型进行充分调查。并在此基础上明晰用水权利边界,加强水资源监测预警机制,通过开发地下水资源,置换出更多可利用水,实现耕地脱盐。
(3) 构建全国盐碱地综合利用云平台。当前中国耕地面积大幅度减少,一些地区盐碱化趋势加剧,盐碱地综合利用迫在眉睫。以往研究集中于形成原因、技术原理、改良措施、作用机制和环境风险评估等方面,而全国盐碱地综合利用模块有待深入构建。基于此,搭建全国盐碱地治理云平台可摸清全国盐碱地现状,有效整合资源,加强“智慧治理”,指导全国盐碱地综合利用试点探索经验模式,进一步推广到类似地区深入论证。
(4) 加强信息技术与水利深度融合。随着人工智能、区块链、智慧水利系统等前沿技术的兴起,地下水动态变化对土壤盐渍化影响的发展应更注重加强智能化管理,掌握水资源动态信息,构建水量分配、调度、预警模型、土壤环境实时监测系统,运用磁共振探测技术、物探技术、同位素示踪等手段推动领域创新发展。目前,中国交叉学科发展相对滞后,应进一步加强前沿学科布局,集中优势解决科学问题,弥补短板,实现地下水数字化监测和精准调控,更好服务于农业生产活动,最终产生更大经济效益和生态效益。
(5) 深入探究地下水调控对土壤包气带水盐运移的影响机制。在干旱和半干旱地区,包气带水占水资源总量70%以上,其中的土壤水盐运移是一个复杂过程。然而,目前对于不同水位调控处理下各剖面盐分变化响应机理尚不明确。因此,应围绕“植物—土壤—包气带—地下水”系统探究水循环过程及盐分迁移机理,综合考虑土壤质地、包气带岩性、作物需水量、气象条件及下垫面条件等,定量分析“地下水动态调控阈值”。此外,包气带水盐运移数值模型在大尺度范围内的模拟亦有待深入研究,针对土壤包气带水盐运移原位监测的尺度效应的研究有待加强,旨在全面、深入了解包气带水盐运移特征,进而建立水盐动态监测及地下水调控系统,加速土壤盐渍化逆向演替进程,提高盐碱地生产力。
| [1] |
Núñez M, Finkbeiner M. A regionalised life cycle assessment model to globally assess the environmental implications of soil salinization in irrigated agriculture[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(6): 3082-3090. |
| [2] |
Barthel S, Isendahl C. Urban gardens, agriculture, and water management: Sources of resilience for long-term food security in cities[J]. Ecological Economics, 2013, 86: 224-234. DOI:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.06.018 |
| [3] |
杨劲松, 姚荣江, 王相平, 等. 中国盐渍土研究: 历程、现状与展望[J]. 土壤学报, 2022, 59(1): 10-27. Yang Jinsong, Yao Rongjiang, Wang Xiangping, et al. Research on salt-affected soils in China: History, status quo and prospect[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2022, 59(1): 10-27. |
| [4] |
Yao Rongjiang, Gao Qiancheng, Liu Yuxing, et al. Deep vertical rotary tillage mitigates salinization hazards and shifts microbial community structure in salt-affected anthropogenic-alluvial soil[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2023, 227: 105627. DOI:10.1016/j.still.2022.105627 |
| [5] |
张作为, 李宏宇, 付强, 等. 化肥有机肥配施对河套灌区土壤盐分及玉米水肥利用的影响[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2023, 31(5): 1170-1182. Zhang Zuowei, Li Hongyu, Fu Qiang, et al. Effects of combined application of chemical and organic fertilizers on soil salinity and corn water and fertilizer utilization in Hetao irrigation district[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2023, 31(5): 1170-1182. |
| [6] |
Chen Jianli, Li Jin, Zhang Zizhan, et al. Long-term groundwater variations in Northwest India from satellite gravity measurements[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2014, 116: 130-138. DOI:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.02.007 |
| [7] |
Wang Yugang, Xiao Duning, Li Yan, et al. Soil salinity evolution and its relationship with dynamics of groundwater in the oasis of inland river basins: Case study from the Fubei Region of Xinjiang Province, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2008, 140(1/2/3): 291-302. |
| [8] |
高佳, 王文科, 赵明, 等. 毛乌素沙地裸地与植被覆盖下非冻结期土壤水分时空分布特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(6): 34-42. Gao Jia, Wang Wenke, Zhao Ming, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of soil moisture in the non-freezing period under the bare land and vegetation cover in the Mu Us desert[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 34-42. |
| [9] |
杨建锋, 万书勤, 邓伟, 等. 地下水浅埋条件下包气带水和溶质运移数值模拟研究述评[J]. 农业工程学报, 2005, 21(6): 158-165. Yang Jianfeng, Wan Shuqin, Deng Wei, et al. Review of numerical simulation of soil water flow and solute transport in the presence of a water table[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2005, 21(6): 158-165. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2005.06.036 |
| [10] |
高宏远, 刘霞, 高晓瑜, 等. 不同灌排模式下盐渍化土壤盐分及离子迁移规律及均衡分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(2): 361-370. Gao Hongyuan, Liu Xia, Gao Xiaoyu, et al. Analysis of salinity and ions migration law and equilibrium in salinized soil under different irrigation and drainage modes[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 37(2): 361-370. |
| [11] |
赵广兴, 李王成, 高海燕, 等. 不同水分对白茎盐生草(Halogeton arachnoideus)根区土壤水盐动态及其生长的影响[J]. 生态科学, 2023, 42(1): 11-20. Zhao Guangxing, Li Wangcheng, Gao Haiyan, et al. Effects of water on soil water and salt dynamics and growth of Halogeton arachnoideus root zone[J]. Ecological Science, 2023, 42(1): 11-20. |
| [12] |
张文化. 变化环境对石羊河流域地下水动态的影响及其生态环境效应研究[D]. 陕西杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2009. Zhang Wenhua. Groundwater dynamic evolution and its impact on eco-environment under variational environment in Shi Yang River basin [D]. Yangling, Shaanxi: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2009. |
| [13] |
余美, 芮孝芳. 宁夏银北灌区水资源优化配置模型及应用[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2009, 29(7): 181-192. Yu Mei, Rui Xiaofang. Model of water resources optimal allocation and application in the Yinbei irrigation district of Ningxia[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2009, 29(7): 181-192. |
| [14] |
Haj-Amor Z, Bouri S. Subsurface drainage system performance, soil salinization risk, and shallow groundwater dynamic under irrigation practice in an arid land[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2019, 44(1): 467-477. DOI:10.1007/s13369-018-3606-3 |
| [15] |
衡通, 何新林, 杨丽莉, 等. 暗管与竖井排水工程改良新疆盐渍土的设计与效果评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(21): 111-118. Heng Tong, He Xinlin, Yang Lili, et al. Design and effect evaluation of subsurface pipe and vertical shaft drainage project to improve saline soil in Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(21): 111-118. |
| [16] |
尹大凯, 胡和平, 惠士博. 青铜峡银北灌区井灌井排水盐运动数值模拟[J]. 农业工程学报, 2002, 18(3): 1-4. Yin Dakai, Hu Heping, Hui Shibo. Numerical simulation of water-salt movement under well-canal combined irrigation scheme in Qingtongxia Yinbei irrigation district[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2002, 18(3): 1-4. |
| [17] |
崔国屹. 基于文献计量分析的土壤盐渍化研究[J]. 河南科技, 2022, 41(7): 108-111. Cui Guoyi. Study of soil salinization based on bibliometric analysis[J]. Henan Science and Technology, 2022, 41(7): 108-111. |
| [18] |
李阳阳, 李王成, 王洁. 基于文献计量分析的土壤水盐运移研究进展[J]. 节水灌溉, 2022(4): 8-15. Li Yangyang, Li Wangcheng, Wang Jie. Research progress of soil water and salt transport based on bibliometric analysis[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2022(4): 8-15. |
| [19] |
Lu Nan, Li Gang, Luo Yuhu. Based on bibliometric analysis of saline alkali soil improvement technology research status and hot spot analysis[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 692(3): 032073. |
| [20] |
Cuevas J, Daliakopoulos I N, del Moral F, et al. A review of soil-improving cropping systems for soil salinization[J]. Agronomy, 2019, 9(6): 295. |
| [21] |
王忠静, 于蘇越, 许兴. 基于文献计量学的土壤盐渍化研究动态定量综述[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 64(2): 303-317. Wang Zhongjing, Yu Suyue, Xu Xing. Quantitative review of soil salinization research dynamics based on bibliometric analysis[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2024, 64(2): 303-317. |
| [22] |
吕志峰, 张建平, 刘鹏, 等. 基于文献计量的干旱地区地下水领域研究进展[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2022, 44(5): 136-142. Lv Zhifeng, Zhang Jianping, Liu Peng, et al. Research progresses of arid area groundwater based on bibliometrics analysis[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2022, 44(5): 136-142. |
| [23] |
陈悦, 陈超美, 刘则渊, 等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究, 2015, 33(2): 242-253. Chen Yue, Chen Chaomei, Liu Zeyuan, et al. The methodology function of Cite Space mapping knowledge domains[J]. Studies in Science of Science, 2015, 33(2): 242-253. |
| [24] |
钟文娟. 基于普赖斯定律与综合指数法的核心作者测评: 以《图书馆建设》为例[J]. 科技管理研究, 2012, 32(2): 57-60. Zhong Wenjuan. Evaluation about the core authors based on price law and comprehensive index method: Take journal of library development as an example[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2012, 32(2): 57-60. |
| [25] |
Ren Dongyang, Xu Xu, Engel B, et al. A comprehensive analysis of water productivity in natural vegetation and various crops coexistent agro-ecosystems[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 243: 106481. |
| [26] |
Liu Zhongyi, Huo Zailin, Wang Chaozi, et al. A field-validated surrogate crop model for predicting root-zone moisture and salt content in regions with shallow groundwater[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2020, 24(8): 4213-4237. |
| [27] |
Xue Jingyuan, Huo Zailin, Wang Shuai, et al. A novel regional irrigation water productivity model coupling irrigation- and drainage-driven soil hydrology and salinity dynamics and shallow groundwater movement in arid regions in China[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2020, 24(5): 2399-2418. |
| [28] |
Liu Kun, Huang Guanhua, Xu Xu, et al. A coupled model for simulating water flow and solute transport in furrow irrigation[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 213: 792-802. |
| [29] |
Ren Dongyang, Wei Boyu, Xu Xu, et al. Analyzing spatiotemporal characteristics of soil salinity in arid irrigated agro-ecosystems using integrated approaches[J]. Geoderma, 2019, 356: 113935. |
| [30] |
史海滨, 杨树青, 李瑞平, 等. 内蒙古河套灌区水盐运动与盐渍化防治研究展望[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2020, 39(8): 1-17. Shi Haibin, Yang Shuqing, Li Ruiping, et al. Soil water and salt movement and soil salinization control in Hetao irrigation district: Current state and future prospect[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2020, 39(8): 1-17. |
| [31] |
李亮, 史海滨, 贾锦凤, 等. 内蒙古河套灌区荒地水盐运移规律模拟[J]. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(1): 31-35. Li Liang, Shi Haibin, Jia Jinfeng, et al. Simulation of water and salt transport of uncultivated land in Hetao Irrigation District in Inner Mongolia[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2010, 26(1): 31-35. |
| [32] |
陈亚新, 史海滨, 田存旺. 地下水与土壤盐渍化关系的动态模拟[J]. 水利学报, 1997, 28(5): 77-83. Chen Yaxin, Shi Haibin, Tian Cunwang. Dynamic simulation of the relationship between water table and salinization of soil[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1997, 28(5): 77-83. |
| [33] |
窦旭, 史海滨, 苗庆丰, 等. 盐渍化灌区土壤水盐时空变异特征分析及地下水埋深对盐分的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(3): 246-253. Dou Xu, Shi Haibin, Miao Qingfeng, et al. Temporal and spatial variability analysis of soil water and salt and the influence of groundwater depth on salt in saline irrigation area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(3): 246-253. |
| [34] |
Dai Xiaoqin, Huo Zailin, Wang Huimin. Simulation for response of crop yield to soil moisture and salinity with artificial neural network[J]. Field Crops Research, 2011, 121(3): 441-449. |
| [35] |
Yuan Chengfu, Feng Shaoyuan, Huo Zailin, et al. Effects of deficit irrigation with saline water on soil water-salt distribution and water use efficiency of maize for seed production in arid Northwest China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 212: 424-432. |
| [36] |
刘广明, 杨劲松, 李冬顺. 地下水蒸发规律及其与土壤盐分的关系[J]. 土壤学报, 2002, 39(3): 384-389. Liu Guangming, Yang Jinsong, Li Dongshun. Evaporation regularity and its relationship with soil salt[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2002, 39(3): 384-389. |
| [37] |
朱伟, 杨劲松, 姚荣江, 等. 黄河三角洲中重度盐渍土棉田水盐运移规律研究[J]. 土壤, 2021, 53(4): 817-825. Zhu Wei, Yang Jinsong, Yao Rongjiang, et al. Soil water and salt transport in medium and heavy saline soils of Yellow River delta[J]. Soils, 2021, 53(4): 817-825. |
| [38] |
张越, 杨劲松, 姚荣江. 咸水冻融灌溉对重度盐渍土壤水盐分布的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(2): 388-400. Zhang Yue, Yang Jinsong, Yao Rongjiang. Effects of saline ice water irrigation on distribution of moisture and salt content in coastal saline soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(2): 388-400. |
| [39] |
王水献, 董新光, 吴彬, 等. 干旱盐渍土区土壤水盐运动数值模拟及调控模式[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(13): 142-148. Wang Shuixian, Dong Xinguang, Wu Bin, et al. Numerical simulation and control mode of soil water and salt movement in arid salinization region[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(13): 142-148. |
| [40] |
周在明, 张光辉, 王金哲. 干旱半干旱地下水浅埋区水盐运移研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(33): 18930-18932. Zhou Zaiming, Zhang Guanghui, Wang Jinzhe. Research progress on water and salt transport in arid and semi-arid shallow groundwater areas[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(33): 18930-18932. |
| [41] |
刘璐瑶, 张金龙, 张凯, 等. 基于HYDRUS-2D模拟排水暗管布设参数对土壤水盐运移的影响[J]. 人民珠江, 2021, 42(4): 70-77. Liu Luyao, Zhang Jinlong, Zhang Kai, et al. Effect of the subsurface drain parameters on water-salt transport based on HYDRUS-2D[J]. Pearl River, 2021, 42(4): 70-77. |
| [42] |
石培君, 刘洪光, 何新林, 等. 基于HYDRUS模型的暗管排水水盐运移模拟[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(3): 224-231. Shi Peijun, Liu Hongguang, He Xinlin, et al. The simulation of water and salt transportation under subsurface drainage by HYDRUS model[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2019, 37(3): 224-231. |
| [43] |
贺文君. 微咸水灌溉对滨海盐碱土水盐分布和金银花生长的影响[D]. 山东烟台: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所), 2021. He Wenjun. Effect of brackish water irrigation on soil water and salt distribution and honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica Thunb. ) growth in coastal saline land [D]. Yantai, Shandong: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2021. |
| [44] |
刘祯媛, 张体彬, 梁青, 等. 不同浓度微咸水灌溉对土壤水盐分布及冬小麦生长的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2024, 38(1): 378-386. Liu Zhenyuan, Zhang Tibin, Liang Qing, et al. Effects of saline water irrigation with different concentrations on soil water and salt distribution and growth of winter wheat[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2024, 38(1): 378-386. |
| [45] |
王宗志, 王宇, 王坤, 等. 滨海地下水库建设与利用方式对含水层水盐运移规律的影响[J]. 水资源保护, 2023, 39(4): 69-78. Wang Zongzhi, Wang Yu, Wang Kun, et al. Influences of coastal underground reservoir construction and utilization on saltwater and freshwater transport law in aquifers[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2023, 39(4): 69-78. |
| [46] |
马贵仁, 屈忠义, 王丽萍, 等. 基于ArcGIS空间插值的河套灌区土壤水盐运移规律与地下水动态研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(4): 208-216. Ma Guiren, Qu Zhongyi, Wang Liping, et al. Research on soil water and salt movement and groundwater dynamics in Hetao irrigation district based on ArcGIS spatial interpolation[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2021, 35(4): 208-216. |
| [47] |
姬祥祥. 不同土壤水基质势水平下河套灌区玉米膜下滴灌土壤水盐运移特征及其模拟[D]. 陕西杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. Ji Xiangxiang. Soil Water and Salt Transport Characteristics and Simulations Under Mulched Drip Irrigation of Maize with Different Soil Water Matric Potentials in the Hetao Irrigation District [D]. Yangling, Shaanxi: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019. |
| [48] |
Crescimanno G, Garofalo P. Application and evaluation of the SWAP model for simulating water and solute transport in a cracking clay soil[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2005, 69(6): 1943-1954. |
| [49] |
Xing Xuguang, Du Wei, Ma Xiaoyi. Field-scale distribution and heterogeneity of soil salinity in the mulched-drip-irrigation cotton field[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2019, 65(9): 1248-1261. |
| [50] |
Morgan K, Jankowski J, Taylor G. Structural controls on groundwater flow and groundwater salinity in the Spicers Creek catchment, Central West Region, New South Wales[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2006, 20(13): 2857-2871. |
| [51] |
Li Xiaobin, Kang Yaohu, Wan Shuqin, et al. Response of Symphyotrichum Novi-belgii and Dianthus chinensis L. to saline water irrigation in a coastal saline soil[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2016(203): 32-37. |
| [52] |
Li Hongfang, Wang Jian, Liu Hu, et al. Quantitative analysis of temporal and spatial variations of soil salinization and groundwater depth along the Yellow River saline-alkali land[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(12): 6967. |
| [53] |
Zhang Yuting, Hou Kai, Qian Hui, et al. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of Northwest China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 837: 155808. |
| [54] |
Mooney S J. Three-dimensional visualization and quantification of soil macroporosity and water flow patterns using computed tomography[J]. Soil Use and Management, 2002, 18(2): 142-151. |
| [55] |
Carrillo M L K, Letey J, Yates S R. Unstable water flow in a layered soil II. effects of an unstable water-repellent layer[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2000, 64(2): 456-459. |
| [56] |
Kulasekera P B, Parkin G W. Influence of the shape of inter-horizon boundary and size of soil tongues on preferential flow under shallow groundwater conditions: A simulation study[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 91(2): 211-221. |
| [57] |
Healy R W. Simulating water, solute, and heat transport in the subsurface with the VS2DI software package[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2008, 7(2): 632-639. |
| [58] |
Havranek R E, Snell K E, Davidheiser-Kroll B, et al. The soil water isotope storage system (SWISS): An integrated soil water vapor sampling and multiport storage system for stable isotope geochemistry[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2020, 34(12): e8783. |
| [59] |
张妙仙, 杨劲松. 灌溉入渗条件下农田土壤水盐动态简化模型及应用[J]. 土壤学报, 2002, 39(1): 75-82. Zhang Miaoxian, Yang Jinsong. The simplified model of salt-water regime in cropland soil under infiltration condition and its application[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2002, 39(1): 75-82. |
| [60] |
李玮, 王立, 姜涛. 地下水浅埋区盐碱地滴灌条件下土壤盐分运移研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2007, 25(5): 130-135. Li Wei, Wang Li, Jiang Tao. Progress of the study on salt transport in saline soil under drip irrigation condition in shallow groundwater area[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2007, 25(5): 130-135. |
| [61] |
朱成立, 徐雨琳, 黄明逸, 等. 基于AquaCrop模型的冬小麦咸淡轮灌制度模拟与评价[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(4): 330-342. Zhu Chengli, Xu Yulin, Huang Mingyi, et al. Simulation and evaluation of cycle irrigation with brackish and fresh water for winter wheat based on AquaCrop model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(4): 330-342. |
| [62] |
黄亚捷, 李贞, 卓志清, 等. 用SahysMod模型研究不同灌排管理情景土壤水盐动态[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(11): 129-140. Huang Yajie, Li Zhen, Zhuo Zhiqing, et al. Soil water and salt dynamics under different irrigation and drainage management scenarios based on SahysMod model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(11): 129-140. |
 2024, Vol. 44
2024, Vol. 44 

